GeoJSON: The Definition and Benefits of a Popular Geospatial Format
GeoJSON has emerged as the go-to format for encoding geospatial data structures using JavaScript Object Notation (JSON). It has gained widespread popularity in the geospatial community and is now considered the standard for representing and exchanging geospatial data on the web. With its support for various types of geometries, such as points, lines, and polygons, GeoJSON allows for the inclusion of properties and additional attributes for each feature.
Understanding GeoJSON: A Primer on Geospatial Data Formats
GeoJSON is a format for encoding geospatial data structures using JavaScript Object Notation (JSON). It is widely used in the geospatial community and has become the standard for representing and exchanging geospatial data on the web. GeoJSON supports various types of geometries, such as points, lines, and polygons, and can also include properties and additional attributes for each feature.
With its simplicity and compatibility with web technologies, GeoJSON has gained popularity among developers, GIS professionals, and data scientists. It allows for easy integration with mapping libraries, such as Leaflet and Mapbox, making it an ideal format for visualizing and analyzing geospatial data.
Furthermore, GeoJSON's human-readable structure makes it easy to create, read, and edit geospatial data. Its syntax is straightforward and follows the JSON format, which means it can be easily parsed and manipulated using programming languages like Python, JavaScript, and Ruby.
In summary, GeoJSON is a flexible and accessible format that simplifies the storage, exchange, and analysis of geospatial data.
The Advantages of GeoJSON: Why It's the Go-To Format for Geospatial Data
There are several advantages to using GeoJSON as the go-to format for geospatial data:
1. Easy Integration: GeoJSON can be seamlessly integrated with web mapping libraries, making it effortless to display and interact with geospatial data on web applications.
2. Lightweight: GeoJSON files are compact and have a smaller file size compared to other geospatial formats like Shapefile or KML. This makes them ideal for web-based applications, as they can be quickly loaded and transmitted over the internet.
3. Interoperability: GeoJSON is a widely supported format across different platforms and tools. It can be easily converted to other formats and used in various GIS software and databases.
4. Attribute Support: GeoJSON allows for the inclusion of attributes and properties associated with each geospatial feature. This enables the storage of additional information, such as names, descriptions, or numerical values, alongside the geometries.
5. Versatility: GeoJSON supports different types of geometries, including points, lines, polygons, and multi-geometries. This versatility makes it suitable for representing a wide range of geospatial data, from simple markers to complex boundaries.
Overall, the advantages of GeoJSON make it a preferred choice for geospatial data management, analysis, and visualization.
GeoJSON vs Other Geospatial Formats: A Comparison
When comparing GeoJSON with other geospatial formats, several factors come into play:
1. File Size: GeoJSON files tend to have a smaller file size compared to formats like Shapefile or KML, which can be advantageous for web-based applications and data transfer.
2. Attribute Support: GeoJSON allows for the storage of attributes and properties alongside the geometries, providing more flexibility compared to formats that only store geometries.
3. Compatibility: GeoJSON is compatible with various web mapping libraries and programming languages, making it easier to work with compared to formats that require specific software or libraries.
4. Geometry Types: GeoJSON supports a wide range of geometry types, including points, lines, polygons, and multi-geometries. Other formats may have limitations or require additional steps to handle certain geometries.
5. Conversion: GeoJSON can be easily converted to other formats, such as Shapefile or GeoPackage, using tools and libraries available in the geospatial community.
Ultimately, the choice of geospatial format depends on the specific use case, data requirements, and compatibility with the tools and systems being used.
DeepBlock.net and GeoJSON: Enhances Geospatial Analysis
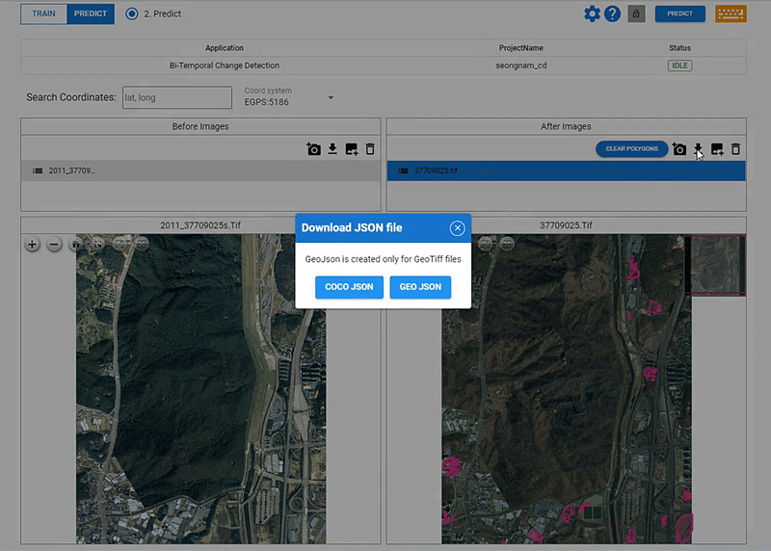
DeepBlock.net, with its support for GeoJSON export, empowers users to leverage the benefits of this popular geospatial format in their analysis workflows.
By exporting data in GeoJSON format, users can seamlessly integrate their geospatial data with other platforms, tools, and services that support GeoJSON. This interoperability enables efficient data sharing, collaboration, and analysis across different GIS software, web applications, and databases.
Furthermore, DeepBlock.net's GeoJSON export feature ensures that the spatial integrity and attributes of the data are preserved during the export process. This means that users can rely on the accuracy and reliability of the exported GeoJSON files for their geospatial analysis tasks.
Whether it's visualizing real estate data, conducting urban planning analysis, or performing location-based analytics, DeepBlock.net's support for GeoJSON export enhances the flexibility and usability of geospatial data for a wide range of applications.
In summary, DeepBlock.net's integration with GeoJSON export empowers users to unlock the full potential of their geospatial data by enabling seamless interoperability and analysis across different platforms and tools.
Real-World Applications of GeoJSON: Exploring Its Versatility
GeoJSON's versatility makes it applicable in various real-world scenarios:
1. Web Mapping: GeoJSON is widely used for creating interactive maps on websites and web applications. It allows for the display of markers, lines, polygons, and other geometries, enabling users to explore and interact with geospatial data in a user-friendly manner.
2. Mobile Applications: GeoJSON is also compatible with mobile application development frameworks, making it suitable for location-based services and applications. It enables developers to incorporate geospatial data and features into mobile apps, such as navigation, geotagging, and augmented reality.
3. Data Sharing: GeoJSON's interoperability makes it an ideal format for sharing geospatial data between different organizations, systems, and databases. It simplifies the process of data exchange and collaboration, facilitating the integration of geospatial data from multiple sources.
4. Geospatial Analysis: GeoJSON can be utilized for various geospatial analysis tasks, such as spatial clustering, proximity analysis, and spatial statistics. Its compatibility with popular data analysis tools, such as Python's GeoPandas or R's sf package, makes it a valuable format for data scientists and analysts.
5. Internet of Things (IoT): GeoJSON's lightweight nature and compatibility with web technologies make it suitable for IoT applications. It enables the representation and analysis of geospatial data collected from IoT devices, such as sensors or GPS trackers, facilitating real-time monitoring and decision-making.
These are just a few examples of the wide range of applications where GeoJSON can be leveraged. Its versatility and compatibility with various platforms and tools make it a valuable format for geospatial data management and analysis.